Daily-Programmer-Bot
Maximal Square – Wednesday October 25th 2020
Given a 2D binary matrix filled with 0’s and 1’s, find the largest square containing only 1’s and return its area. Example:
Input:
1 0 1 0 0
1 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
1 0 0 1 0
Output: 4
Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days – Wednesday October 26th 2020
A conveyor belt has packages that must be shipped from one port to another within D days.
The i-th package on the conveyor belt has a weight of weights[i]. Each day, we load the ship with packages on the conveyor belt (in the order given by weights). We may not load more weight than the maximum weight capacity of the ship.
Return the least weight capacity of the ship that will result in all the packages on the conveyor belt being shipped within D days.
Example 1:
Input: weights = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], D = 5
Output: 15
Explanation:
A ship capacity of 15 is the minimum to ship all the packages in 5 days like this:
1st day: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
2nd day: 6, 7
3rd day: 8
4th day: 9
5th day: 10
Note that the cargo must be shipped in the order given, so using a ship of capacity 14 and splitting the packages into parts like (2, 3, 4, 5), (1, 6, 7), (8), (9), (10) is not allowed.
Example 2:
Input: weights = [3,2,2,4,1,4], D = 3
Output: 6
Explanation:
A ship capacity of 6 is the minimum to ship all the packages in 3 days like this:
1st day: 3, 2
2nd day: 2, 4
3rd day: 1, 4
Example 3:
Input: weights = [1,2,3,1,1], D = 4
Output: 3
Explanation:
1st day: 1
2nd day: 2
3rd day: 3
4th day: 1, 1
Constraints:
• 1 <= D <= weights.length <= 50000
• 1 <= weights[i] <= 500
Binary Tree Postorder Traversal – Wednesday October 27th 2020
Given the root of a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes’ values.

Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [3,2,1]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]

Example 4:
Input: root = [1,2]
Output: [2,1]
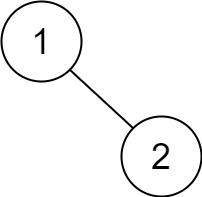
Example 5:
Input: root = [1,null,2]
Output: [2,1]
Binary Tree Postorder Traversal – Wednesday October 28th 2020
Given a positive integer n, find the least number of perfect square numbers (for example, 1, 4, 9, 16, ...) which sum to n.
Example 1:
Input: n = 12
Output: 3
Explanation: 12 = 4 + 4 + 4.
Example 2:
Input: n = 13
Output: 2
Explanation: 13 = 4 + 9.
Kth Largest Element in an Array – Wednesday October 29th 2020
Find the kth largest element in an unsorted array. Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not the kth distinct element. Example 1:
Input: [3,2,1,5,6,4] and k = 2
Output: 5
Example 2:
Input: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] and k = 4
Output: 4
Note: You may assume k is always valid, 1 ≤ k ≤ array’s length.
Number of Operations to Make Network Connected – Wednesday October 23th 2020
Implement a first in first out (FIFO) queue using only two stacks. The implemented queue should support all the functions of a normal queue (push, peek, pop, and empty).
Implement the MyQueue class:
• void push(int x) Pushes element x to the back of the queue.
• int pop() Removes the element from the front of the queue and returns it.
• int peek() Returns the element at the front of the queue.
• boolean empty() Returns true if the queue is empty, false otherwise.
Notes:
• You must use only standard operations of a stack, which means only push to top, peek/pop from top, size, and is empty operations are valid.
• Depending on your language, the stack may not be supported natively. You may simulate a stack using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a stack’s standard operations.
Follow-up: Can you implement the queue such that each operation is https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amortized_analysis|amortized O(1) time complexity? In other words, performing n operations will take overall O(n) time even if one of those operations may take longer.
Example 1:
Input
["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
Output
[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
Explanation
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
Constraints:
• 1 <= x <= 9
• At most 100 calls will be made to push, pop, peek, and empty.
• All the calls to pop and peek are valid.